What is
toenail fungus?
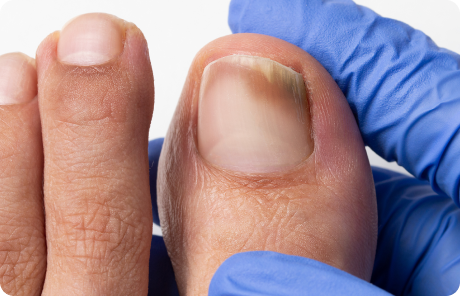
Nail fungus, or onychomycosis, is a fungal infection, usually of the toenails, that is progressive and generally does not go away on its own. Fungal nail infections are estimated to account for up to 50% of all nail problems. The numbers are thought to be higher for the elderly. Proper detection, diagnosis and early treatment can help speed up recovery and prevent permanent damage to the nail.
Dermatologists Explain
“Be patient when treating nail fungus. Once the infection progresses beyond a certain point, the treatment will take time to work.”
“Don’t neglect your nails. If your nail has changed in appearance without knowing why, have a doctor check it. A fungal infection becomes progressively more challenging to treat with time.”
How to identify toenail fungus
Some typical signs that you might have a fungal toenail infection are:
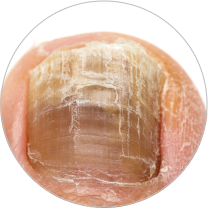
Toenails that are brittle and crumbly
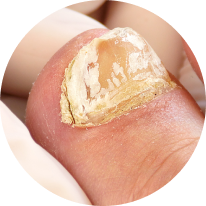
Yellow, white or brown nail discolouration
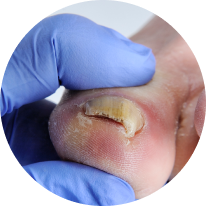
An accumulation of debris under the nail
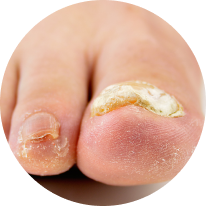
Toenails that become thicker
Why you should treat a toenail fungus infection
This is a common nail infection that often results in nail plate damage, deformity, and toenail dystrophy that can interfere with walking, exercise, or proper shoe fit. These can occur as the nails thicken when the infection progresses, and it may become uncomfortable to wear closed shoes and to walk, exercise or stand. Thus, early treatment is recommended before the infection becomes more severe or has spread to other toenails.
Although nail fungus rarely causes serious health risks, the toenail can also become a fungal reservoir. This can lead to recurrent fungal infections of the skin, such as athlete’s foot, that can cause fissures or cracks, leaving the feet more vulnerable to secondary bacterial infections. People with a weakened immune system, due to diabetes or peripheral vascular disease for example, may be more susceptible to both fungal infections and other secondary infections, such as cellulitis.
Lastly, toenail fungus can be transmitted from person to person. This may happen in your home and in high-risk areas, such as locker room floors and public pools. By treating your toenail fungus and by limiting exposure by not going barefoot, you can avoid transmitting the fungus to others.
Possible complications of toenail fungus
As a fungal infection progresses, the toenail may become painful and thicker, and the fungus may spread to other nails and the surrounding skin, causing athlete’s foot.
It is better to treat a toenail infection early before it becomes severe and harder to treat.
These are some typical signs that your toenail fungus infection is becoming more severe:
- Continued toenail discolouration: yellow to a darker colour
- Continued brittleness and crumbling
- Possible pain under the toenail
- Further toenail thickening
- Spreading of the infection to other nails
- Spreading of the infection to the surrounding skin
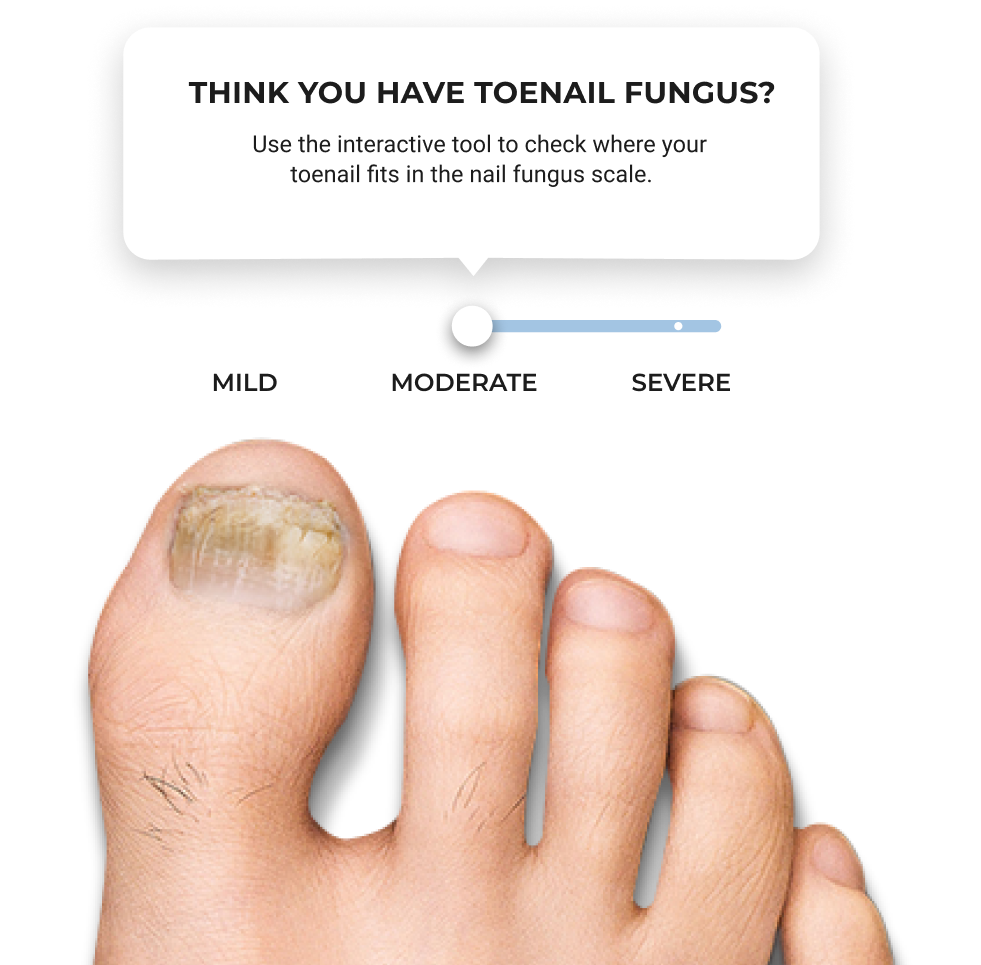
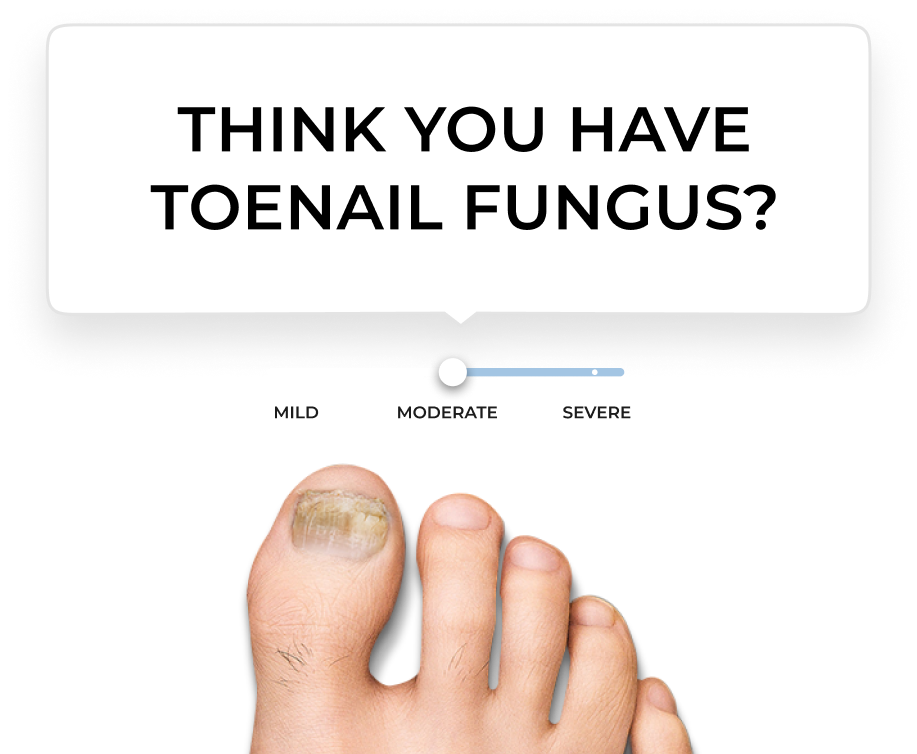
Think you have
toenail fungus?
Use our tool to check your symptoms and evaluate if you may have visual signs of a toenail fungus infection. See a doctor to have a diagnosis and ask which treatment option is appropriate for you.
Check if you havethe symptoms